The world of pottery admixtures
As can be seen in the pottery of Fukui Cave, the mixing of parts of plants or fibres extracted from them into the clay used when making pottery had already begun in the Incipient Jomon period. This was done as a way to strengthen the pottery and thus to make it more lightweight. In the Ento-doki culture of the area from northern Tohoku to southern Hokkaido, pottery containing large amounts of plant fibres was made. Although this practice was not consistent, it is a phenomenon that can be seen during specific times throughout Japan.
Pottery from the Early Jomon period has been found mainly in the Hidaka region of Hokkaido that shows the impressions of cord (rope). Since the knots in the cord have been identified, we assume that nets of rope were probably used to make these marks. CT scanning of these particular sections of the pottery has allowed us to observe twisted cords and the knots in these cords in more three-dimensional images.
In addition, approximately 10,000 years ago, when wild rice began to be used in China, earthenware vessels with embedded rice in their husks appear, a practice that was to continue for quite a long time. The same type of impressions have been observed in pottery found at sites dated to the beginning of the Yayoi period. However, while these pottery pieces have millet and shiso (Perilla frutescens var. crispa) mixed into their clay, it remains unknown whether rice in its husk was mixed in the clay in China for the same purpose as in Japan. The presence of these types of by-products of grain processing that were used in pottery-making may indicate the spread of farming culture. This issue requires further study in the future.

3D images of potsherds included plant remains from Fukui cave site in Sasebo City (15,000 BP)

3D images of pottery embedded with several species of seeds from Kozako site in Shibushi City (2,700 BP)
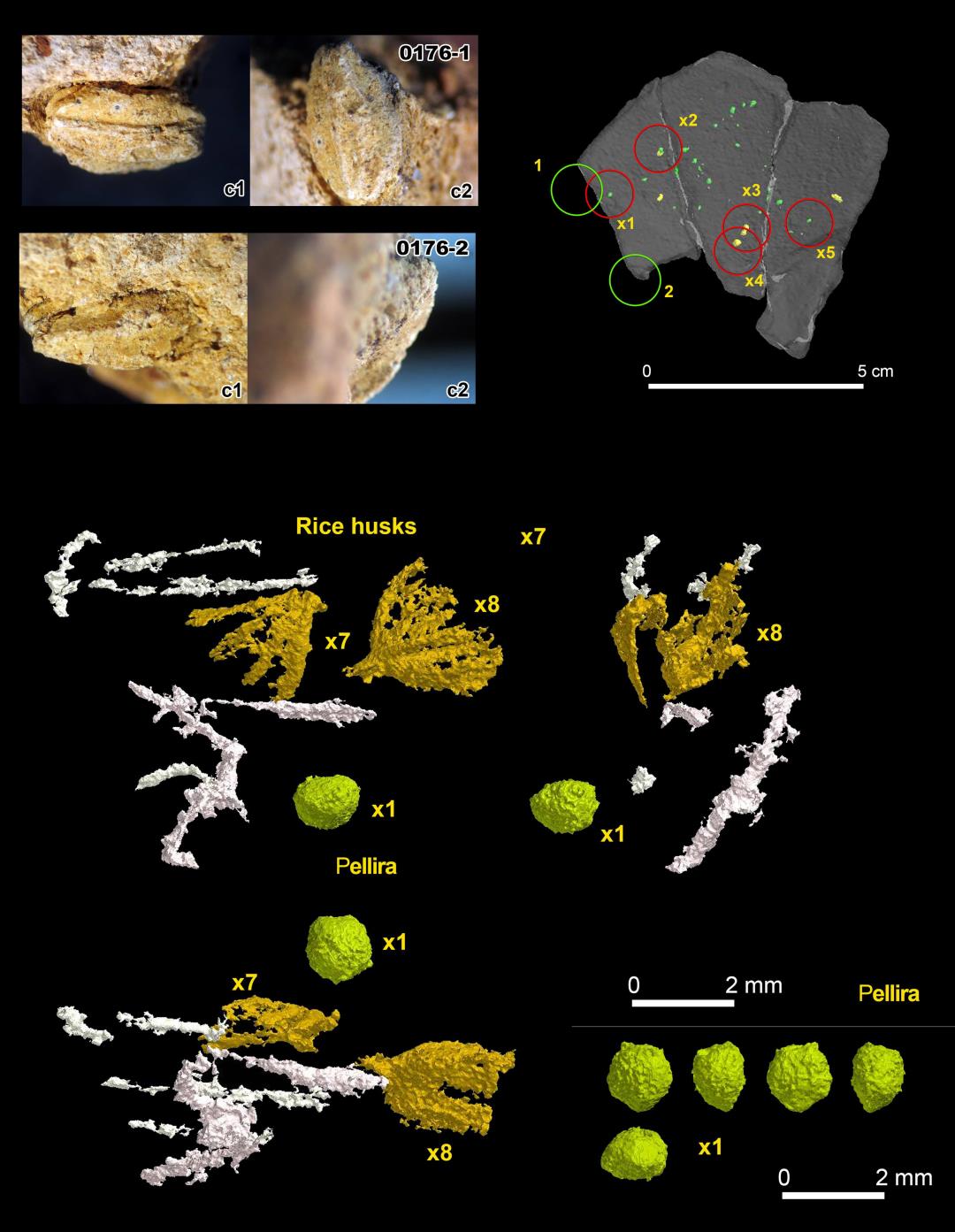
3D and SEM images of pottery embedded with several species of seeds from Kurostuchi site in Miyakonojo City (2,500 BP)

3D images of potsherd mixed with rice husks from Uchihashi-tsubomi site in Kasuya-machi (2,000 BP)

3D image of pottery included rice husks from Ezuko site, No. 9 in Kumamoto City (2,500 BP)
3D image of potsherd No. 1 included plant remains from Fukui cave site in Sasebo City (15,000 BP)
3D image of potsherd No. 2 included plant remains from Fukui cave site in Sasebo City (15,000 BP)
3D image of pottery included rice husk from Ezuko site, No. 9 in Kumamoto City (2,500 BP) “Let’s looking for the rice husks!”
3D image of potsherd mixed with several species of seeds from Kozako site in Shibushi City (2,700 BP)
3D image of potsherd mixed with several species of seeds from Kurotsuchi site in Miyakonojoi City (2,500 BP)